 An Advertising Budget refers to the amount of money allocated towards advertising of a brand or product.
An Advertising Budget refers to the amount of money allocated towards advertising of a brand or product.
While developing an advertising strategy, it is empirical to set advertising objectives which are significantly influenced by the advertising budget. Advertising objectives are important for decision making and to have a point of reference or standard against which the results can be measured. A business may choose a sales objectives or communication objectives for the purpose of developing an advertising budget.
(i) Sales Objectives – The objective is to increase the sale of products or to compliment the selling efforts of the sales department. The objective may be changed from time to time depending upon the volume of sales which may be influenced by –
- Price of products
- Advertising and Promotion
- Personal selling
- Competition
- Consumer tastes
- Product quality
- Economy
- Technology
- Direct action advertising
(ii) Communication objective – The objective is to create awareness, develop interest or to change an attitude. For this purpose a business may choose to –
- Increase the % of target customers who associate a special feature or benefit with company’s brand
- Increase number of customers who prefer company’s brand over competing brands
- Increase company’s brand usage among existing members
- Encouraging a brand trial among targeted customers
Basis of Advertising Budget
The various factors that have to be studied before setting the advertising budget are –
- Market size and Potential
- Product life cycle stage
- Market share
- Intensity of competition
- Advertising frequency
- Product differentiation strategies
Many businesses consider advertising as an expense rather than an investment, hence it is important to use a theoretical basis and budget allocation methods to make an effective advertising budget.
The Theoretical basis for creating an advertising budget is Economic Marginal Analysis. According to Economic Marginal Analysis a firm should continue to increase its advertising budget for a particular brand or for a certain target market as long as the (MR) Marginal Revenue exceeds the Incremental Expenditure (IE). However this basis takes into account the two assumptions which are:
- Advertising is solely responsible for sale
- Sales are a direct result of advertising and the deviation can be measured accurately
Due to these assumptions this model is rarely used as it is not practical to that assume advertising alone determine sales as there are many other environmental factors that affect sales.
Most advertiser support one of two models of advertising to sales response function namely the Concave downward function or the S-shaped function.
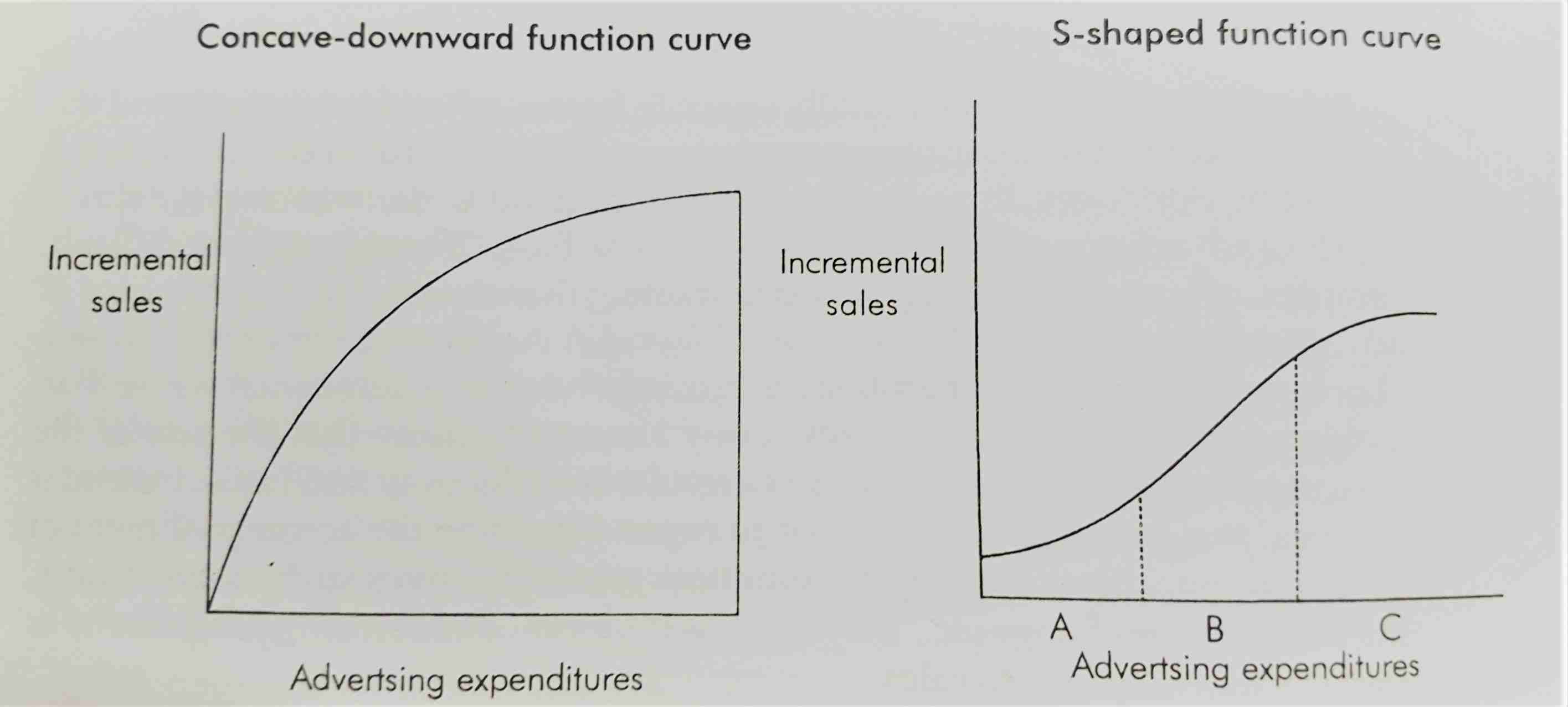
Picture Credits: Advertising and Sales Promotion – S.H.Kazmi, Satish.K.Batra
Concave downward function curve – As the amount of advertising increases it incremental value decreases following the law of diminishing marginal utility i.e. advertising effects start diminishing quickly. Hence less advertising money may needed for optimum sales.
S-shaped function curve – Initial expenditure on advertising has a very little effect on sales. After a certain point increment in advertising expenditure lead to increased sales but the gain in sales continue only up to a point and after that there is no effect on increased expenditure on sales. Hence it suggests that less budget has a minimal impact and a high budget may not necessarily have a high impact.
Advertisers must advertise and spend in the area of rising curves where maximum return on advertising expenditure can be accomplished.
Approaches to Advertising Budget
Approaches to Advertising Budget | |
| Top Down Approach | Build Up Approach |
| Top management sets the spending limit | Advertising objectives are set |
| Advertising budget is set within the allocation limits. | Activities necessary to achieve objectives are planned |
| Advertising objectives and activities are planned according to the set budget. | Costs of different advertising elements are budgeted. |
| It is a Judgmental Approach | Total advertising budget is approved by top management |
| Budget is not linked to the objectives. | Budget is allocated on the basis of activities considered essential to accomplish the objectives. |
| This leads to predetermined budget allocations which are not related to advertising objectives. | |
| Methods – Affordable Method, Arbitrary Allocation, Percentage of Sales, Competitive parity, Return on investment | Methods – Objective and Task Method, Payout Planning, Quantitative Approach, Experimental Approach |
Methods of Advertising Budget
(i) The affordable method – All you can afford –
- It is a simple method
- Whatever is left out of the financial budget is allocated to advertising
- After making all business expenditures the amount left is allocated to advertising
- No consideration is given to advertising objectives or goals
- Chances of over or under spending are high
- A common method in small firms or firms with primary focus on new product development
(ii) Arbitrary Allocation Method –
- There is no theoretical basis of creating a budget
- Budget is allocated on the basis of what is felt necessary by decision makers
- It lacks systematic thinking
- There is no relationship with advertising objectives
- Managers believe that some amount must be spent on advertising and pick up a figure
(iii) Percentage of sales method –
- It is a commonly used method by large and medium sized companies
- Budget allocated depends upon the total sales figure i.e. high sales = high budget, low sales = low budget
- The basis of budget allocation is the total sale of brand or product. It may be:
- A fixed percentage of last year’s sales figure is allocated as the budget.
- A fixed percentage of projected sales figures of the next year
- A fixed amount of the unit product cost is taken as advertising expense and multiplied by the number of projected sales unit.
Advantages
- It is simple, straight forward, easy to implement
- Expenditures are directly related to funds available.
Disadvantages
- It ignores that less advertising may decline sales or potential of advertising in rising sales
- It can lead to over or under spending
- It is difficult to predict sales for new products
- Decrease in sales leads to decrease in advertising budget which may be needed
(iv) Competitive parity method –
- Budget is based on competitors expenditure, advertisers decide budget matching competition’s % of sales allocation
- Information of competitor`s budget is available in trade journal and business magazine
- The basis is that collective wisdom of many firms may generate an advertising budget optimum or close to optimum
- It leads to competitive stability
- It minimizes chances of promotional wars
Disadvantages
- Each firm allocates budget according to its own specific goals
- It ignores the contribution of media and creative executions
- Information is gathered when money is spent
(v) Objective and Task method
In this method the selling objectives and budget decision are linked and considered simultaneously. It involves –
- Defining the advertising communication objectives to be accomplished
- Deciding specific strategies and tasks necessary to achieve them
- Estimating the costs involved in putting these activities in operation
- The total of these costs is taken as the base to determine the advertising budget.
Advantages
- The method develops budget from ground up which is a proper managerial approach
- It does not rely on past sales or future sale forecasts
- It considers all factors under advertiser’s control
Disadvantages
- It is difficult to implement
- It requires managerial involvement and high skills
- It attempts to introduce variables such as awareness, knowledge, attitude formation etc.
- It is difficult to estimate all costs and determine all tasks necessary to achieve the set objectives
(vi) Pay out planning
- It is useful when introducing a new product
- The aim is to spend heavily to achieve increased awareness and product acceptance
- It estimates the investment value of advertising by linking it to other budgeting methods
- The idea is to predict the amount of revenue the product will generate and the costs it will incur over a period of time
- The advertising budget is determined on the basis of rate of return desired
- Preparing a payout plan depends upon accuracy of sales forecast, factors affecting market, estimated costs
- Initially the advertising expenditures will be high and eventually will reach a break-even point and then will show decline and increase in sales following the S shaped Function
Advantages
- It is useful and logical planning tool
Disadvantages
- It cannot account for uncontrolled factors e.g. – competition, changes in government policies, new technology
(vii) Quantitative Models
- Advertisers use quantitative methods such as mathematical and statistical models to allocate advertising budget
- Multiple regression analysis is used to determine the effect of advertising expenditure on sales.
- Experimentation and formal analysis is required to use this method
- It is an expensive and time consuming method
(viii) The Experimental approach –
- It is an alternative to quantitative models
- The Advertising manager conducts tests or experiments in one or more selected market areas
- The Advertising strategy is tested in market areas with similar population, brand usage, market share
- Different advertising expenditure levels are kept for each market
- Brand awareness and sales levels are measured before and after
- Results are compared and variation of influence of advertising expenditure studied
- The feedback results determine the advertising budget levels
- Manager may decide a certain budget level according to the advertising objectives
Disadvantages
- It is expensive and time consuming
- It ignores uncontrollable factors
- It not universally accepted