A budget is a financial and quantitative statement of an operational plan related to a specific time period, which is to be followed during the budgeted period in order to achieve specific financial objectives of an organization.
According to I.C.W.A, “A budget is a financial and/or quantitative statement prepared prior to a defined period of time, of the policy to be pursued during that period for the purpose of attaining a given objective.”
Features of a Budget
- It is a financial and quantitative statement of a plan of action
- It is always expressed in terms of money and/or quantity
- It is prepared prior to the implementation of the operational plan
- It is based on pre-determined management policy
- It is prepared to achieve specific financial objectives
- It indicates the costs and revenues, capital to be employed, incremental effects on former budgets etc.
Budgeting
Budgeting refers to the process of preparation, implementation and operation of budgets. It involves formulation of operational plans for a given future period and expressing it in monetary terms.
Types of Budget
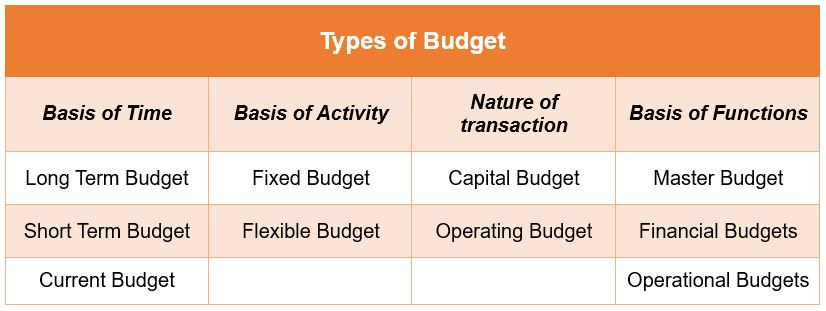
On the Basis of Time
- Long Term Budget – Budget prepared for a period of 5 to 10 years.
- Short Term Budget – Budget prepared for a period of 1 to 2 years.
- Current Budget – Budget prepared for a period of less than 6 months.
On the Basis of Activity
- Fixed Budget – Budget that is fixed for a given level of activity or time period and does not change with changing business situations.
- Flexible Budget – Budget that is flexible and can be revised from time to time according to the changing business needs and situations.
On the Basis of Nature of transaction
- Capital Budget– Budget prepared for the capital expenditures of a business.
- Operating Budget – Budget prepared to meet the day to day expenses of a business.
On the Basis of Functions
Master Budget – Various functional budgets are integrated together to form a master budget.
Financial Budgets – Budgets related to various costs and revenues of the organization.
- Cash Budget
- Working Capital Budget
- Capital Expenditure Budget
- Income Statement
- Budgeted Balance Sheet
- Retained Earnings
Operational Budgets – Budgets prepared for different activities or operations of the organization.
- Sales Budget
- Production Budget
- Purchase Budget
- Materials Budget
- Personnel Budget
- Plant Utilization Budget
- Marketing Budget
- Administrative & Selling expenses budget
- Manufacturing Expenses budget
Budgetary Control
Budgetary Control is the process of determining various budgeted figures for an organization for the future period and then comparing the budgeted figures with actual figures for calculating deviations and taking remedial measures to minimize deviations. It is a continuous process that helps in planning and controlling costs.
According to Howard and Brown, “Budgetary control is a system of controlling costs which includes preparation of budgets, coordination of departments, comparison of actual performance with budgeted performance and acting upon the results to achieve maximum profitability.”
Requirements of a Good Budgetary System
- Budgeting process must be backed by the Chief Executive of an organization
- Organizational goals must be clearly stated and quantified and further divided into functional goals
- People responsible for execution of budget must be involved in its preparation
- Budgets must be realistic, continuous and must cover all relevant aspects
- Budgeting system must be based on information, communication and participation
- Clear responsibilities for effective budget implementation must be established
Essentials of Budgetary Control
(1)Organization Structure
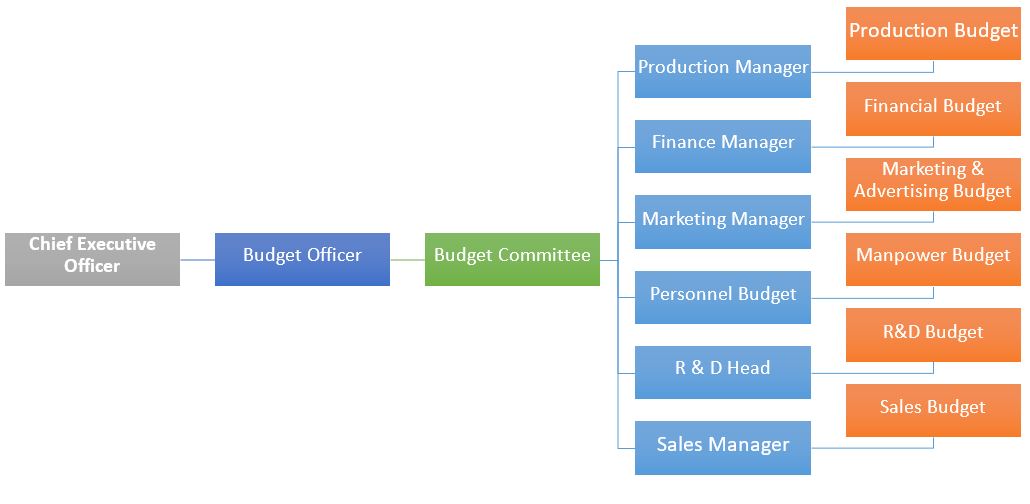
(2) Budget Centers – It may be a department or a group of people in a department, who are responsible for preparation of a budget.
(3) Budget Manual – It is a written document containing rules, regulation, policies and guidelines for preparing budgets.
(4) Budget Officer (Coordinator) – The person responsible for scrutinizing, evaluating and finalizing the budgets prepared by different functional heads.
(5) Budget period – Time period for which budget is prepared.
(6) Budget Committee – Group of people responsible for preparation and execution of budgets
(7) Determining Key Factor – Principle factor that influences all budgets
Steps in Budgetary Control System
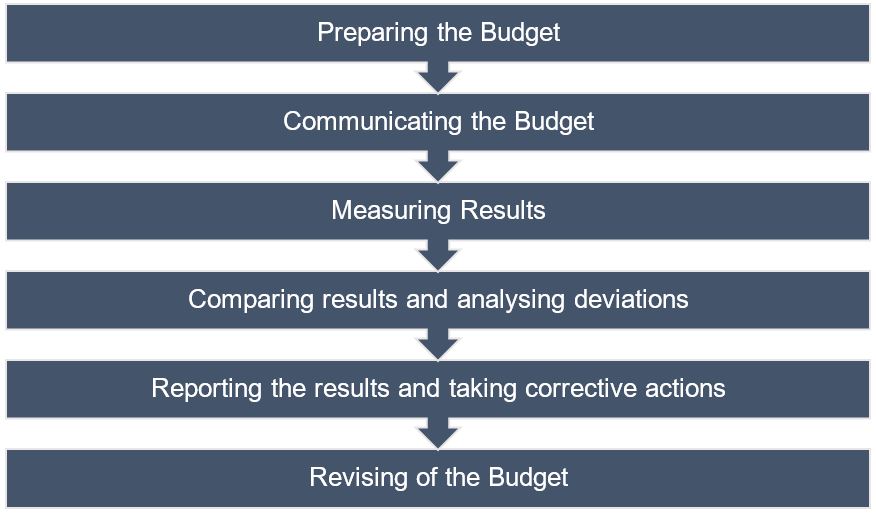
Advantages of Budgetary control
- Effective budgetary control leads to maximization of profit
- It facilitates coordination between different functional departments
- It acts as a tool for measuring (financial and operational) performance
- It helps in eliminating wastages and taking corrective actions
- It helps in reducing costs
- It helps to take decisions regarding performance appraisal of employees
Also Read: