Investment: It refers to the employment of funds on assets with the aim of earning income or capital appreciation. It has two attributes i.e. Time & Risk. It is essentially a sacrifice of current money or other resources for future benefits.
Speculation – It involves taking calculated business risks for the purpose of earning short-term profits. It involves buying and selling of assets with expectations of getting profits from price fluctuations.
Gambling – It involves taking artificially created risk in a game of chance.
Investment Objectives
- Return – Income from investment
- Risk – Risk of an investment refers to the variability of returns from different investment alternatives
- Liquidity – It depends upon marketability and trading facilities associated with an investment. It refers to the ease of converting as an asset into liquid cash
- Hedge against Inflation – Returns from investments provide protection against inflationary tendencies present in the economy
- Safety – Investment alternatives are subjected to a sound legal and regulatory framework
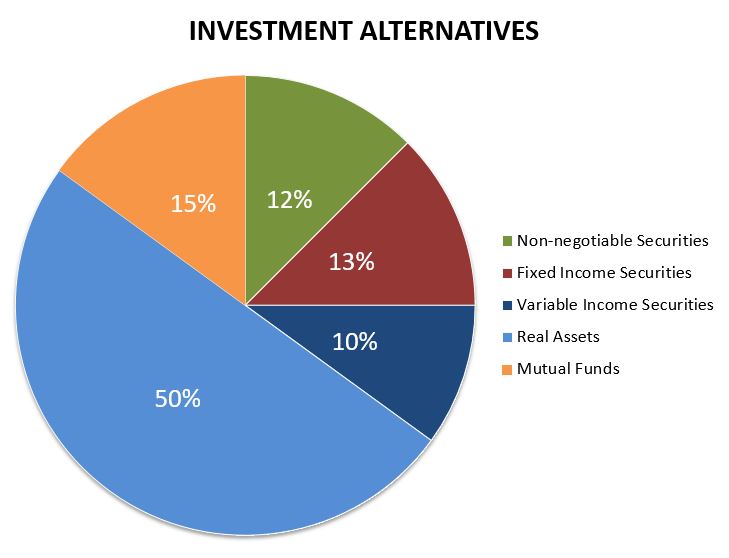
Investment Alternatives: Negotiable and Non-negotiable Securities
Investment Process
- Framing of Investment policy – Funds, Objectives, Knowledge
- Investment Analysis – Economic Analysis, Market Analysis, Industry Analysis, Company Analysis
- Valuation – Industrial value and Future Value
- Portfolio construction – Diversification, Selection and allocation of funds to an optimum mix of various debt and equity instruments.
- Portfolio Evaluation – Appraisal and Revision
(1) Framing of investment policy – Before making any investment one must formulate an investment policy for systematic functioning. The main components of an investment policy include –
- Investible Funds – Availability of funds, Source of funds i.e. Savings or borrowing (if funds are borrowed then the rate of return on investment must be higher than the rate of borrowing)
- Objectives – Required rate of return, Need for regular income, risk perception, need for liquidity, capital appreciation or safety of principle
- Knowledge – One should be aware of different investment alternatives, various stock markets, and financial structure of the country and must have sufficient knowledge regarding functions of brokers, mode of operations, related taxes and charges etc.
(2) Investment Analysis – After a suitable investment policy has been formulated, the next step is to conduct market, industry as well as company analysis to scrutinize the securities one plans to buy.
- Market Analysis – A market analysis helps an investor to understand the general economic scenario. Economic variables like Gross domestic product (GDP), inflation, Recession etc. help an investor to depict stock prices and stock trends and fluctuations. One can set entry and exit points through technical analysis.
- Industry Analysis – An industry analysis helps analyze the economic significance and growth potential of an industry. Factors like growth rate, growth potential and contribution of an industry in an economy helps an investor to make an informed decision.
- Company Analysis – Knowledge regarding a company`s earnings, profitability, operating efficiency, capital structure, top management, market share etc. is essential for an investor, as these factors have a direct impact on the stock prices of the company and the return to investors. Companies with high market share are capable of creating wealth in form of capital appreciation for an investor.
(3) Valuation – The next step is to determine the expected risks and returns from an investment. The intrinsic value of a share is measured through the book value and price-earnings ratio of a share. The intrinsic value of a share is then compared with its market value to make an investment decision. An effort is made to determine the future value of the investment.
Intrinsic value = Book Value + P/E Ratio compared with the market price
(4) Portfolio Construction – A portfolio is a combination of different securities. A portfolio must be constructed in such a way that it meets the investor`s needs and objectives with the aim to deliver maximum returns with minimum risk. The goal is to create an optimum mix of debt and equity instruments. The reduce the risk and ensure the safety of principal a portfolio is diversified by creating a portfolio with an optimum mix of debt and equity instruments, securities from different companies and industries are chosen on the basis of expected returns. In the end, funds are allocated to the selected securities.
(5) Evaluation – Portfolio performance is periodically evaluated to measure and compare the variability of returns from different securities. Portfolio appraisal involves evaluating the portfolio with respect to two key dimension – Risk and Return. On the basis of appraisal results, revisions are made to the portfolio. Low yielding securities with high risk are replaced with low risk and high yielding securities. This process is done periodically to keep stable returns.