According to sec 2(20) of the companies act, 2013 “’A company is a company formed under the companies Act 2013 or under any of the previous acts relating to companies.”
A company may be defined as “an incorporated association which is an artificial person, having a separate legal entity, with a perpetual succession, a common seal, a common capital compromised of transferable shares and limited liability.”
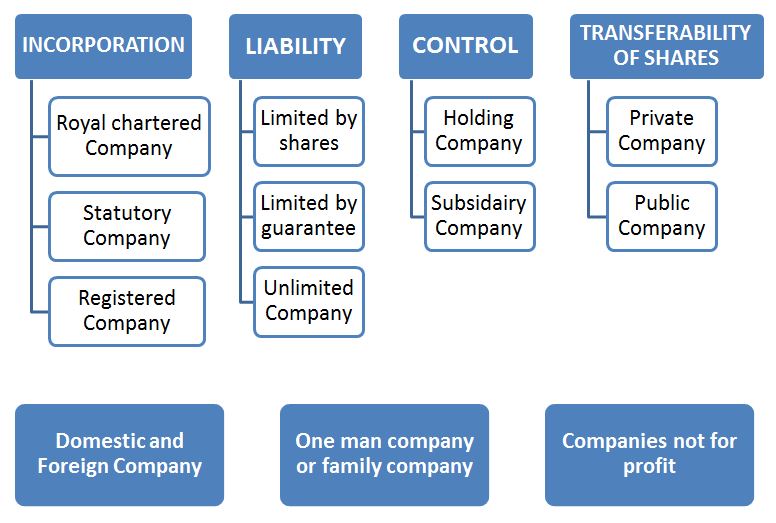
Kinds of Companies
The various Kinds of companies that can be formed under the Companies Act, 2013 are:
On The Basis of
The following are the different kinds of companies that can be formed under the Companies Act –
Royal Chartered Company – These are companies formed under the Royal Charter of a company or by a special order of king or queen. Eg. East India Company formed by the Royal Charter of Great Britain. Such a company derives its nature on the basis of the charter under which they are formed.
Statutory Company – It is incorporated by a special Act passed either by the Central or State legislature. Companies intended to carry on some business of national importance are formed this way to provide a service to its citizens. Eg. RBI formed under RBI Act 1934.
Registered Companies – A company registered under the companies Act 2013 or any other existing Act. It is governed by the companies Act 2013.
Company limited by shares – It is a company in which the liability of the members (shareholders) limited i.e. they are only liable for the unpaid value of shares held by the member. The unpaid amount can be called upon any time during the life time or winding up of the company. If the shares of a member are fully paid up then his liability will be nil.
Company limited by Guarantee – In such a company the Liability of shareholders is limited up to the amount guaranteed or invested by the shareholder towards the assets of the company in the event of its being wound up. The amount guaranteed can be only demanded at the time of its wound up, hence it is a reserve capital. Such companies are generally formed to promote art, science, commerce, sports etc. and are not for profit making.
Unlimited companies – A company having no limit on the liability of its Shareholders is an unlimited company. Thus the liability may extend to the personal property of the Shareholders in case the company is not able to satisfy its claims at the time of winding up. This liability of members is like a partnership where they have to contribute according to the ratio of amount invested in the company.
Holding and Subsidiary company – Where one company controls the management of another company, the former is called the holding company and the later over which the control is exercised is termed as a subsidiary company.
- A company shall deemed to be a holding company of another, if that other is a subsidiary
- A company shall be deemed to be subsidiary of another company if the other company –
- Controls the composition of its Board of Directors.
- Holds more than half of nominal value of equity share capital.
- It is a subsidiary of another company which is another company’s subsidiary.
- If it holds more than 50% of the total voting rights of the company.
Private Company – The term “private company” has been defined under section 2(68) of Companies act 2013. A private company means a company, which has a minimum paid up share capital of Rs. 1 lakh and which provides the following restrictions through its Articles of Association and Memorandum –
- Restricts the transfer of shares by its members
- Limits the maximum number of members to 50
- Prohibits any invitation or acceptance of public deposits
- Prohibits invitation to public for debentures of the company
It enjoys special privileges also –
- It can be started with only 2 members (minimum members)
- It is not required to prepare a prospectus and it can start its operations immediately after receiving the certificate of incorporation.
Public company – The term ‘public company’ has been defined under section 2(71)of Companies act 2013. A ‘public company’ means a company which has minimum paid up share capital of Rs. 5 lakh and which is not a private company. It has the following features –
- It does not restrict transferability of shares
- At least 7 members are required to form a public company
- There is no restrictions on the number of members
- It has atleast 3 directors
- Its name end with the word “limited”
- It can accept public deposits and invite public for subscription of its shares and debentures
A private company which is a subsidiary of a public company will also be considered a public company under this Act
Domestic company – A company which is based in India registered under the Companies Act 2013. The head Office and its business operations are conducted within the country. It can either be private or public.
Foreign company – A Foreign company is a company incorporated outside India which establishes its business operations within India under the Companies Act 2013. Within 30 days of its establishment, it has to furnish important documents to the registrar as per Sec 380. They are:
- A certified copy of the charter of the company
- Memorandum and Articles of Association of the company
- Address of the registered office
- List of directors and secretary
- Full address of the principle place of business in India
- Name and address of the authorised person to do business on behalf of the company in India.
One Man Company – Where one man holds practically the whole of the share capital of a company and takes a few more dummy members simply to meet the statutory requirements of the minimum number of persons such a company is one man company. A one man company can be incorporated under sec 2(62) of the Companies Act, 2013. In such a company the principle shareholder is the virtual owner running the business with limited liability and other members may have even one share.
Companies not for profit – These companies must obtain a license from the central government before they are registered. They are limited liability but are not required to use the word Limited or private with their names.
They are formed promoting art, science, commerce, sports etc. Profits are applied towards its objective and cannot be distributed among its members.
- It enjoys various exemptions on registration.
- It does not pay stamp duty for registration of Memorandum and Articles of Association.
- It can be formed without share capital
- Government can revoke license any time by giving a notice
copy
To protect our content from misuse, we do not allow users to copy content from our site, But you can always bookmark (CTRL + D) the site for instant access.
screenshot knocked your door
the max limit of members in pvt company is 50 and in public company its 200 and you have mentioned it vice versa.
Hi kritika, we believe this will clear you doubts –
According to Section 2, Clause 68 of Companies Act 2013,
“private company” means a company having a minimum paid-up share capital of one lakh rupees or such higher paid-up share capital as may be prescribed, and which by its articles,— (i) restricts the right to transfer its shares; (ii) except in case of One Person Company, limits the number of its members to two hundred: Provided that where two or more persons hold one or more shares in a company jointly, they shall, for the purposes of this clause, be treated as a single member: Provided further that— (A) persons who are in the employment of the company; and (B) persons who, having been formerly in the employment of the company, were members of the company while in that employment and have continued to be members after the employment ceased, shall not be included in the number of members; and (iii) prohibits any invitation to the public to subscribe for any securities of the company.”
It’s minimum… The minimum member required for private company is 50 and maximum is 200
nice
NICE ESSAY
Nice article..
However, the total number of minimum and maximum members in
Private company: minimum 2 members – maximum 50 members
PUBLIC company: minimum 7 members- no maximum number of members
Thanks for the update
Hey,
Thanks for the Beautiful Post. I found the required information in detail manner for further steps in your post.