Segmentation of Market (Market Segmentation) is concerned with dividing the total heterogeneous population into smaller homogeneous groups of customers who share similar needs and wants. Through market segmentation organizations identify different groups of customers in the market that can be targeted effectively with specific products and services and through a specific marketing mix (4p`s strategy).
A market segment is a subset of the market which consists of individuals or organizations which have similar needs and demand similar products and services due to their specific demographic, psychographic, behavioral or socio-cultural characteristics.
The process of segmentation of market starts with research and analysis of the market to identify key target groups and then each group is evaluated in order to find out the most potential segments or groups.
An organization makes specific product, price, distribution and promotion decisions that cater to their target audience, therefore it is important to carefully evaluate each segment on the basis of its future profit potential and only the most profitable segments should be targeted.
Techniques of Segmentation of Market
(1) Priori segmentation – It is the most basic way to segment a market. A priori segmentation involves division of the market according to existing demographic criteria such as age, gender, occupation, lifestyle etc. A priori segmentation technique is generally used when a product or service has a strong relationship any demographic criteria e.g. there is a strong relationship between age and use in case of baby products, toys, higher education etc.
(2) Usage Segmentation – It involves segmenting the customers according to their frequency of usage of a product or service like heavy users, light users, ex-users, potential users, regular users etc. This type of segmentation focuses on the activities of a customer related to a product and his level of involvement in the product. It is usually considered in terms of time and place for example, clubs offer free drinks and discounts for few hours a day (happy hours) or a day of the week on the basis of frequency of visits and amount of customers present at a time or day.
(3) Attitudinal and Cluster segmentation – It is concerned with dividing the market into customer segments with similar attitude toward a product, service, industry etc. Usually likert scales are used to determine how different attitudes affect a purchase decision and then Cluster analysis is conducted to group people with similar attitudes. Thus market is segmented into homogeneous groups on the basis of what customers think, how they feel and how they behave towards a particular set of marketing mix.
(4) Need based Segmentation – This technique of market segmentation focuses on the needs, wants and motives of the consumers. Conjoint analysis is used to divide people into different groups on the basis of key drivers and specific needs & requirements that motivate a person to make a purchase. After identifying the target audience, they are segments into customers with similar needs and preferences through cluster analysis. Need based segments are the most actionable and stable groups that help in estimating existing and future market share.
Basis of Segmentation of Market
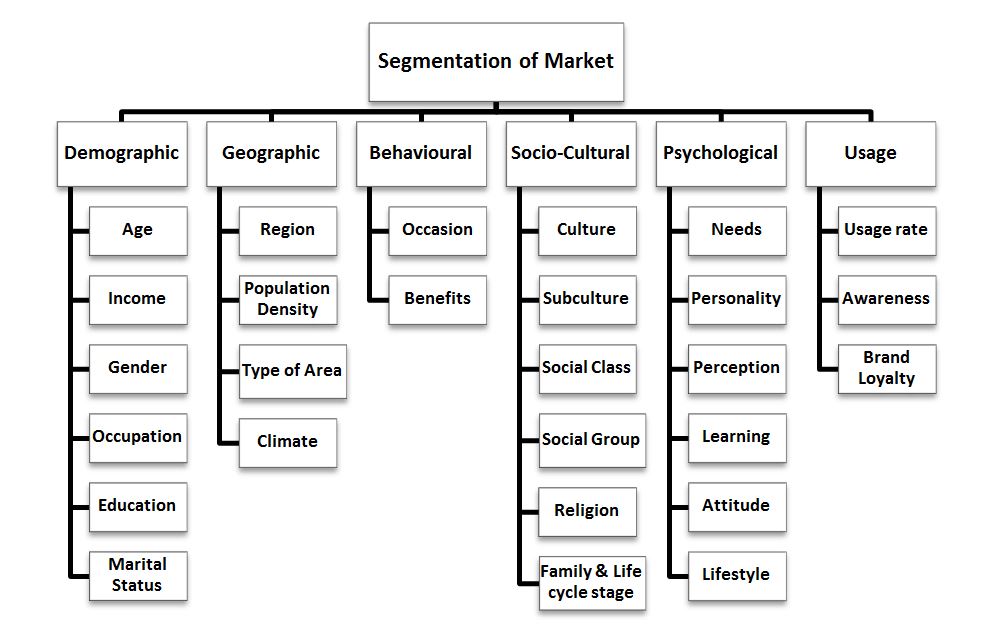
(1) Geographic Segmentation –
- Region – North, South, East, West
- Population density – Metropolitan areas, small cities, villages, towns
- Type of Area – Urban, suburban, exurban, rural
- Climate – Cold, hot, humid
(2) Demographic Segmentation –
- Age and Life cycle stages – Baby, teenager, bachelor, parent, grand-parent
- Gender – Male, Female
- Marital Status – Single, married, divorced, living together, widowed
- Income – Lower, middle, upper
- Education – High school, graduate, post-graduate
- Occupation – Salaried worker, businessmen, professionals
(3) Psychological/Psycho-graphic Segmentation –
- Needs – Shelter, safety, security, love, self-esteem, self-actualization
- Personality – Extrovert, introvert, aggressive, compliant
- Perception – Safe players, moderate risk takers, high risk takers
- Learning- Low involvement, high involvement
- Attitudes – Positive attitude, negative attitude
- Lifestyle – Achievers, Strugglers, Strivers, Makers
(4) Socio-cultural Segmentation –
- Culture – Indian, American, Japanese, Chinese, Mexican
- Subculture – Shia and Sunni, Brahmin and Kshatriya
- Religion – Hinduism, Islam, Sikhism, Christianity
- Social Class – Lower class, middle class, upper-middle class, upper class
- Family Role – Buyer, Initiator, User, Disposer
- Lifecycle Stage – Bachelors, young marrieds, empty nesters
(5) Use-Related Segmentation –
- Usage Rate – Heavy users, regular users, light users, 1st time user, non-users
- Awareness – Unaware, aware, informed, interested, desire, intend to buy
- Brand Loyalty – Brand Loyalists, Brand Switchers
(6) Behavioural Segmentation –
- Occasion – birthdays, marriages, festivals, national events, holidays
- Benefits – Convenience, prestige, economy, value-for-the money, Quality, speciality